HMO, PPO, EPO, POS: What’s the Difference?

You’ve probably heard of HMOs and PPOs because they are the more popular types of health plans. But what are they? What are the differences among them? What other options are available? What are the advantages and disadvantages of each? And, most importantly, how do you decide which one is best for you? Well, you’ve come to the right place.
First, it's helpful to understand that a provider network can be made up of doctors, hospitals and other health care providers that have agreed to offer negotiated rates for services to participants of certain medical insurance plans.
HMO
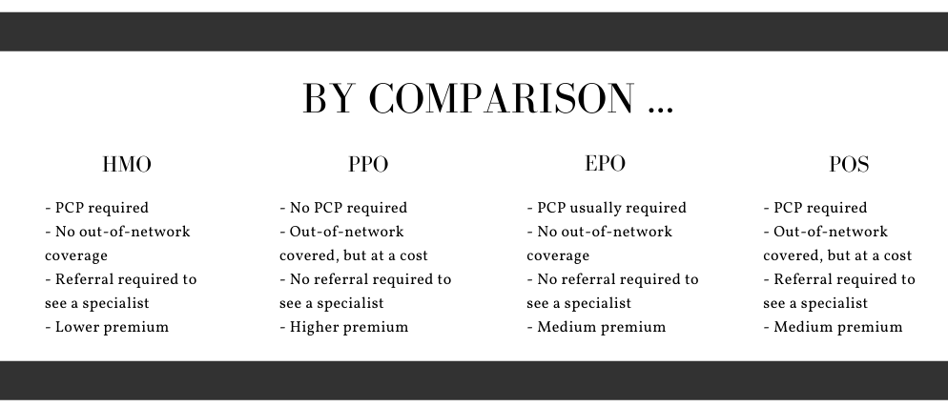
A Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) is a type of health plan that has a restricted network of doctors and hospitals. It requires that patients see their primary care physician (PCP) first to get a referral to see a specialist. If you think you need to see a cardiologist, for instance, you’ll have to visit your doctor first. The cardiologist will also have to be within the HMO network for the costs to be covered.
Out-of-network doctors, hospitals, and lab facilities are not covered, except in the case of a medical emergency. (Like a skiing accident while visiting Colorado, for instance.) If you enroll in an HMO, your costs — copay, premium, and deductible — will likely be lower than with a PPO or EPO health plan, but you’ll be more restricted in the kind of care you receive.
Just as HMO participants are limited to a network of doctors, the same is true for pharmacies. Patients must have prescriptions filled at an in-network location to be covered.
Pros: Generally lower premiums than a PPO
Cons: Must stay in network, need referral to see a specialist
PPO
A Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) is a health plan that has a larger, “preferred” network of providers, giving you more flexibility in choosing a doctor or hospital. Out-of-pocket costs tend to be higher with a PPO. You also do not need a referral to see a specialist; you’ll be able to book the appointment on your own. These plans usually offer more comprehensive coverage. PPO plans often cover some portion of out-of-network doctors, hospitals, and lab work, though you’ll pay more than if you visit an in-network provider.
You are also covered if you receive care out of state if the provider is considered in network. So, if you have a chronic health condition that means seeing specific providers, or a family history of a condition for which you want to see a specific specialist, a PPO plan might be a good option.
You can determine who is considered “in network” by calling your insurance carrier. The phone number is on the back of your health insurance card, usually listed as “Member Services.”
When it comes to prescriptions, PPOs allow patients to fill a script almost anywhere, though you may pay more if using an out-of-network pharmacy.
Pros: Larger network, don’t need referral to see a specialist, can go out of network
Cons: Generally higher premiums
EPO
An Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) doesn’t require a referral to see a specialist, but it doesn’t cover out-of-network providers like a PPO does, except in the case of an emergency. Participants must use providers from a specified network of physicians and hospitals to get coverage. Because they offer less flexibility than PPOs, EPOs usually have less expensive premiums.
Pros: Don’t need referral to see a specialist
Cons: Must stay in network, limited network
POS
A Point-of-Service (POS) is a hybrid between an HMO and a PPO. It’s sometimes referred to as an “open-ended” HMO when offered. POS plans resemble HMOs for in-network services. A referral is required to see a specialist. Services received outside of the network are usually reimbursed like conventional-provider reimbursement based on a fee schedule.
Pros: Can go out of network for care
Cons: Need referral to see a specialist, must file claims for out-of-network care
What to consider
Which plan is right for you? That depends on your specific situation. Here are some factors to consider:
- Your health
- Your family’s health
- Whether your health care providers accept the insurance
- Affordability
- Scope of the network
- Whether you’re concerned about getting a referral to see a specialist
If you’re having trouble deciding which option may be the best fit, give us a call at (724) 349-1919.


Share Your Thoughts